4.3 Application of Working Capital Ratios to Amazon.com
In the previous chapter, we defined
the major working capital ratios:
Accounts receivable turnover = Sales/Accounts Receivables
Inventory turnover = COGS/Inventory
Accounts payable turnover = Purchases/Accounts payable or
otherwise COGS/Accounts Payable
In
addition, turnover ratios are often expressed in terms of number
of days by dividing 365 by the turnover ratio:
Number of days to Collect Accounts Receivable = 365/Accounts
receivable turnover
Number of days to Sell Inventory = 365/Inventory turnover
Number of days to Pay Creditors =365/ Accounts payable
turnover
Finally,
the Cash Conversion cycle is the sum of the first two, the
aggregate number of days for collecting accounts receivable and
the number of days required to sell inventory.
Now, recall that it was 1999 when
Amazon expanded into its own warehouses.
This was the year where the GBF strategy started to take
effect but had a negative impact in the.
This was reflected in Amazon’s inventory management
ratios as follows:
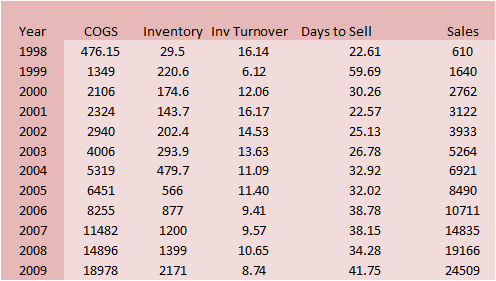
COGS increased sharply in 1999 along
with Sales. However,
the cost of this was the sharp decline in inventory turnover and
increase in days to sell inventory; the days to sell inventory
almost tripled to 59.69 from 22.61.
The impact of the old economy managers is evident in 2000
where the days to sell inventory were almost halved and by 2001
were equal to 1998 levels but with a 600% increase in sales. In
other words, the GBF strategy was back in balance with at least
1998 ratio levels.
Amazon’s other working capital ratios
are as follows:
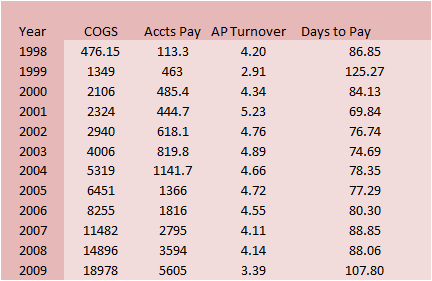
You can see that Amazon increased the
days to paying its payables especially in 1999 when it increased
to 125.27 days; this recovered to the 1998 levels by 2000.
Similarly, on the collection front
Amazon’s 1999 numbers increased sharply.
Overall, it can be seen that Amazon’s working capital
strategy is to attain favorable creditor terms but collect their
payables relatively quickly.
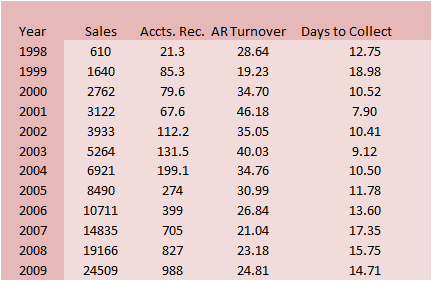
Overall, Amazon’s GBF and expansion in
1999 led to a significant deterioration in their working capital
management which was subsequently rectified by their managers.
