8.23 Residual Operating Income (ReOI)
This income number is defined
as:
ReOI = NOPATt – (Weighted Average Cost of Capital *
Net Operating Assetst-1 )
The weighted average cost of capital was defined in chapter 4. A brief description is provided below: The cost of equity capital for the firm as a whole is different from the cost of equity capital for the stock issued by the firm, and the usual formulation is in terms of the after tax weighted average cost of capital.
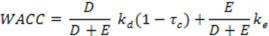
Where τc is the effective corporate tax rate, kd
is the cost of debt capital and ke is the cost of
equity capital. The
weights are usually constructed relative to market values.
The above equation works with the after tax cost of debt
because interest expense is tax deductible whereas dividend
payments are not.
Net Operating Assets (NOA)
is defined as total assets minus operating liabilities for a
segment.
NOA = Total Assets − Operating Liabilities
Operating Liabilities are usually defined in terms of working
capital liabilities such as Accounts Payables, Income Taxes
Payable, Other Current Liabilities, Other Liabilities, Minority
Interest. That is,
liabilities that do not involve the financing decision.
The remaining liabilities and preferred stock if issued,
are referred to as Net Financial Obligations (NFO) and:
Shareholders’ Equity = NOA - NFO
A
closer inspection of the consolidated balance sheet reveals
that:
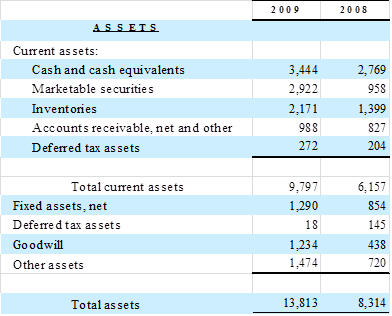
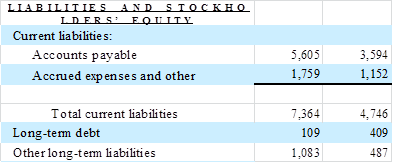
So
as a first pass computing for t-1 (= 2008)
NOA is:
NOA
= 8,314 – 4,746 – 487 = 3,081
Now
calculate ReOI as:
ReOI = NOPATt – (Cost of Equity Capital * Net
Operating Assetst-1 )
We
will allocate 3,081 on the basis of relative proportion of total
assets (e.g., North America = 5266/8314 = 0.633).
We
will assume that the required rate of return for Amazon which
equals the WACC (weighted average cost of capital) is provided
by CAPM = 0.0406 + 1.21*0.051 = .1023 because Amazon has very
little outstanding debt especially when we define the weights by
relative market values of stock and bonds.
If you refer to the WACC equation provided earlier you
will see that the debt weighting is Market Value of Debt/(Market
Value of Debt plus Equity).
The
above inputs for CAPM you can get immediately from Valuation
Tutor by clicking on the relevant parts (e.g., beta from Profile
and either Beta (MSN) or Beta (Yahoo), Bonds MSN to get the
30-year bond rate, and finally “Equity Premium Surver” to get
the current consensus (0.051)).
North America = 510.13 – 3081*(5266/8314)*0.1023 =310.49
International = 620.94 - 3081*(1-(5266/8314))*0.1023 = 505.39
From
the first pass it appears that International performs better
than North America.
This may reflect that they have less competition internationally
or it may also reflect the breakdown of total assets and
especially leased facilities.
It is likely that leased facilities are more prevalent in
the international operations and thus accounting for leases
(i.e., operating versus capitalized) should be considered.
Amazon does not break this out by segment in their 10-K
aand they discuss leases as follows:
Leases
and Asset Retirement Obligations
We categorize leases at their
inception as either operating or capital leases. On certain of
our lease agreements, we may receive rent holidays and other
incentives. We recognize lease costs on a straight-line basis
without regard to deferred payment terms, such as rent holidays
that defer the commencement date of required payments.
Additionally, incentives we receive are treated as a reduction
of our costs over the term of the agreement. Leasehold
improvements are capitalized at cost and amortized over the
lesser of their expected useful life or the life of the lease,
excluding renewal periods. We establish assets and liabilities
for the estimated construction costs incurred under
build-to-suit lease arrangements to the extent we are involved
in the construction of structural improvements or take some
level of construction risk prior to commencement of a lease.
But
note Amazon has been careful to separate out the two segments in
terms of capacity:
International
The International segment
consists of amounts earned from retail sales of consumer
products (including from sellers) and subscriptions through
internationally focused websites such as www.amazon.co.uk,
www.amazon.de, www.amazon.co.jp, www.amazon.fr, and
www.amazon.cn. This segment includes export sales from these
internationally based sites (including export sales from these
sites to customers in the U.S. and Canada), but excludes export
sales from www.amazon.com and www.amazon.ca.
So
it would appear that currently International earns a little more
margin.
