8.11 Application IBM Step 2: Comprehensive Income
Residual income is dollar excess return over what is required by
investors in terms of the cost of equity capital times book value of
shareholders equity. As
a result, it can be expressed as follows:
Residual Earningst Excess Return = (Return on Common
Equityt – Cost of equity capital) * Book value of
common equityt-1
In the above the Return on
Common Equityt (ROCEt) is defined as:
Comprehensive Earningst/Book Value of Common Equityt-1.
The two drivers of residual income are ROCE and Book Value plus to
forecast residual income over time requires an assessment of growth
behavior estimates.
IBM Example:
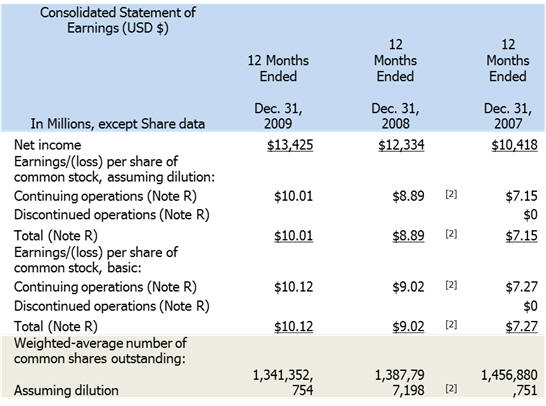
The 10-K Consolidated Income Statement filings from IBM provide the
source data as follows:
Source:
2009 10-K IBM SEC Filing
From the above the Earnings per share = $13.425/1.341 =
$10.011 and as computed earlier the Book Value per Share equals
$16.881.
For Residual Income we are interested in Comprehensive income.
This is defined as follows:
Comprehensive income = Net income + Other Comprehensive income
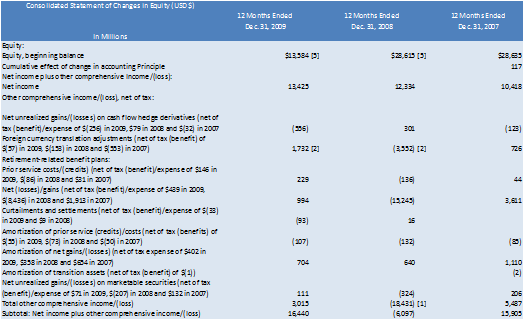
In the 10-K statements the last three years for “Other Comprehensive
Income” is available in the Shareholders Equity Statement.
Conceptual Note:
In dirty surplus accounting some items are adjusted to the
stockholder’s equity as opposed to the income statement.
The main three items are:
foreign currency translation, pension liability and hedge
accounting adjustments.
As a result, these items can fluctuate from year to year and so we
will take the average over the three years provided in the 10-K as a
first pass for “Other Comprehensive Income.”
The three years provided (2009, 2008 and 2007) respectively are:
Important
Note:
Recall that in this exercise
we are interested in calculating Comprehensive income for valuation
purposes. That is, we
want to estimate sustainable comprehensive income such that we can
apply growth behavior to in order to project the future behavior of
comprehensive income.
In practice this requires some judgment calls and in this case it is
evident that the year to year fluctuations are large for Other
Comprehensive Income.
As a result, to provide an estimate that is likely to be sustainable
we take the average:
Other Comprehensive Income = (3015 +( 18431) + 5487)/3 =
(3309.67)
The Comprehensive income that we will apply for valuation purposes
is:
Comprehensive income = $13,425 + ($3310) = $10115 million
Comprehensive Earnings per share = $10.115/1.341 = $7.543 and as
computed earlier in section IV the Book Value per Share equals
$16.881.
