8.10
Application IBM
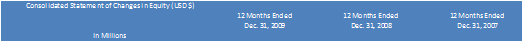
From the
Income Statement the average number of shares outstanding
respectively for:
2009, 2008 and 2007

Note to the above 10-K:
Following FASB Statement 160 (ASC 810-10) the FASB has
recently (beginning on or after December 15, 2008) required that
“noncontrolling interests” are part of equity in a consolidated
reporting entity.
This is a departure from the previous practice of treating
minority interests as a mezzanine item between liabilities and
equity. This
has resulted from the convergence process between US GAAP and
IFRS and in particular aligns reporting of noncontrolling
interests with the requirements in IAS27.
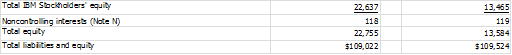
As a result, by working with IBM’s Balance Sheet
from their 10-K we subtract out Noncontrolling interests to
compute the Book Value per Share:
Book Value per Share
= Total Shareholders’ Equity/(Weighted-average number of shares outstanding) = 22.637/1.341 = $16.881 equals the book value per share.
The
accounting concept of “Comprehensive Income” measures the change
in Shareholders’ Equity not involving the shareholders.
It is different from traditional accounting income
because in practice not all items pass through the accounting
income statement.
For example, foreign currency translation adjustments,
derivative accounting and certain pension liability adjustments.
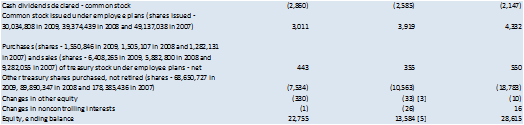
Dividends, Treasury stock acquisitions and any new stock
issues are not included because these involve the shareholders.
Comprehensive income is reported in the Consolidated
Statement of Stockholders’ Equity in a standard 10-K form.
The book value per share (BV) is the Shareholders’ Equity
divided by shares outstanding.
This can change for several reasons, including the
payment of dividends, issuance of new shares.
